Packaging is everywhere in our daily lives. It protects the things we buy, makes them look good, and gives us important information. But there’s more to packaging than meets the eye. In this blog, we’ll explore the world of packaging, from its types and materials to its role in business and the move toward sustainability.
What Is Packaging?
Packaging is the process of designing and producing containers or coverings for products. It serves three main purposes:
- Protection: Keeps items safe during transportation and storage.
- Communication: Shows details like product name, ingredients, and usage instructions.
- Marketing: Attracts customers with appealing designs.
Types of Packaging
Packaging is divided into three levels:
| Type | Purpose | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Packaging | Directly touches the product. Keeps it safe and usable. | A water bottle, a chocolate wrapper |
| Secondary Packaging | Groups multiple primary packages together. | A box of 6 water bottles |
| Tertiary Packaging | Used for bulk shipping or storage. | Pallets, shrink wrap |
Common Packaging Materials
Different materials are used for packaging based on the product and its needs:
| Material | Used For | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Paper/Cardboard | Lightweight, recyclable. | Cereal boxes, cartons |
| Plastic | Flexible, durable, and versatile. | Grocery bags, bottles |
| Glass | Sturdy, good for food and drinks. | Jam jars, soda bottles |
| Metal | Long-lasting, used for preservation. | Cans, tins |
| Wood | Strong, reusable for large items. | Crates, pallets |
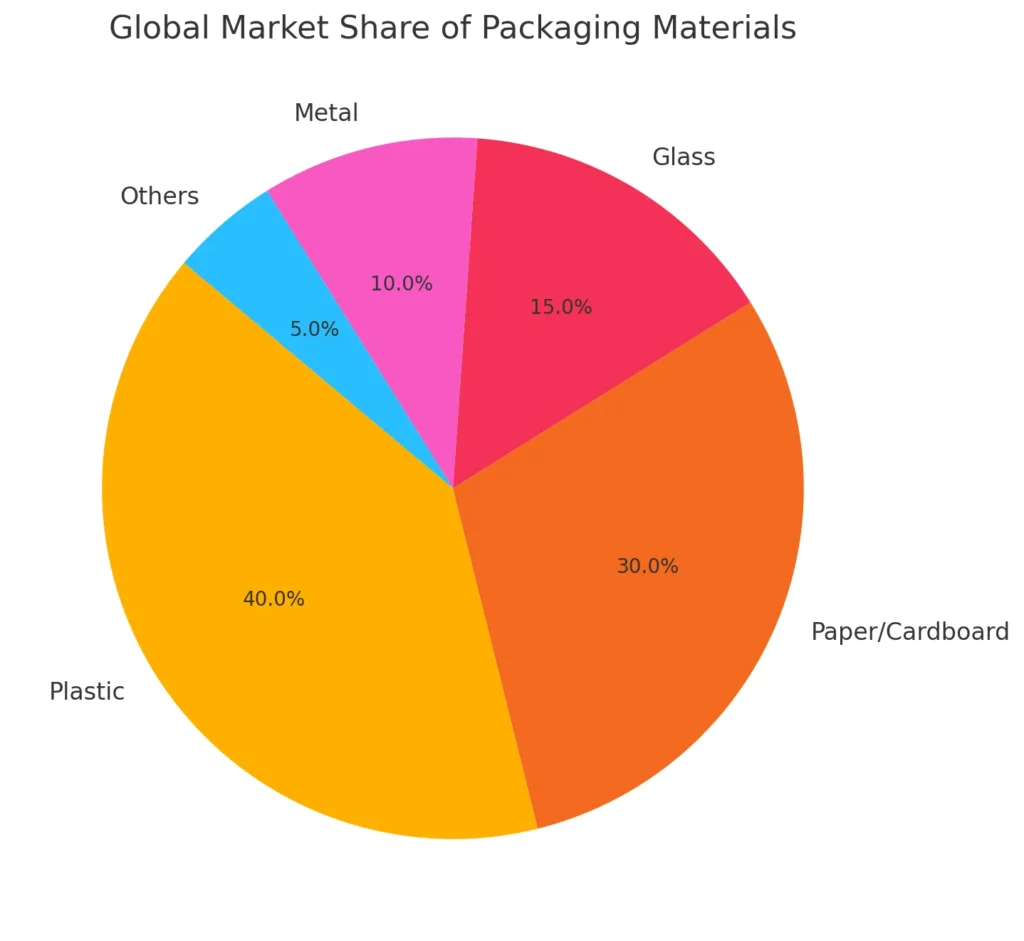
Visual Insight: Global Market Share of Packaging Materials
The chart below shows how different materials dominate the packaging market.
Why Packaging Matters
Packaging is more than just wrapping. Here’s why it’s so important:
- Protecting Products:
- Keeps items safe from damage, dirt, or bacteria.
- Example: Bubble wrap protects fragile items like glass.
- Providing Information:
- Displays details like expiration dates, usage instructions, or nutritional facts.
- Example: A food label lists ingredients and allergens.
- Attracting Customers:
- Eye-catching packaging can grab attention on shelves.
- Example: A colorful cereal box appeals to kids.
- Brand Recognition:
- Logos and designs make products easily recognizable.
- Example: Coca-Cola’s red label is iconic.
Sustainable Packaging: The Future
With environmental concerns rising, companies and consumers are focusing on eco-friendly options.
Key Features of Sustainable Packaging:
- Recyclable: Can be reused, like cardboard and certain plastics.
- Biodegradable: Breaks down naturally over time, such as plant-based materials.
- Minimalist: Uses less material to reduce waste.
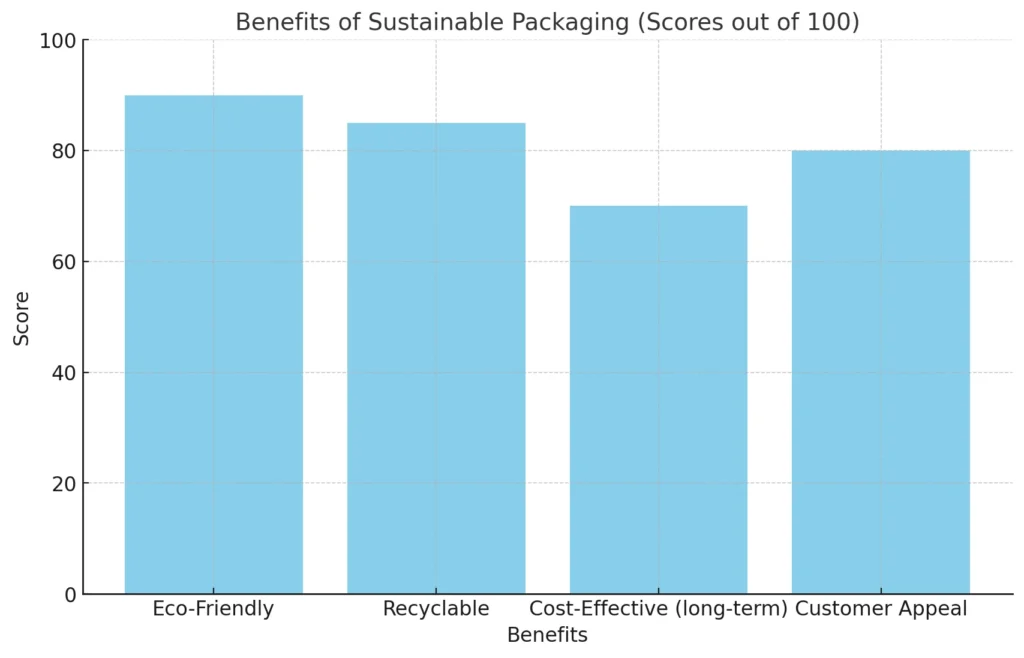
Benefits of Sustainable Packaging
Sustainable packaging offers multiple benefits, as shown in the chart below.
Trends in Packaging
- Smart Packaging:
- Technology-enabled packaging that tracks freshness or product usage.
- Example: QR codes on food packages linking to recipes.
- Minimalist Design:
- Clean, simple designs to reduce visual clutter.
- Example: Brands like Apple focus on clean, sleek boxes.
- Reusable Packaging:
- Packaging that can be used multiple times, like glass jars or metal tins.
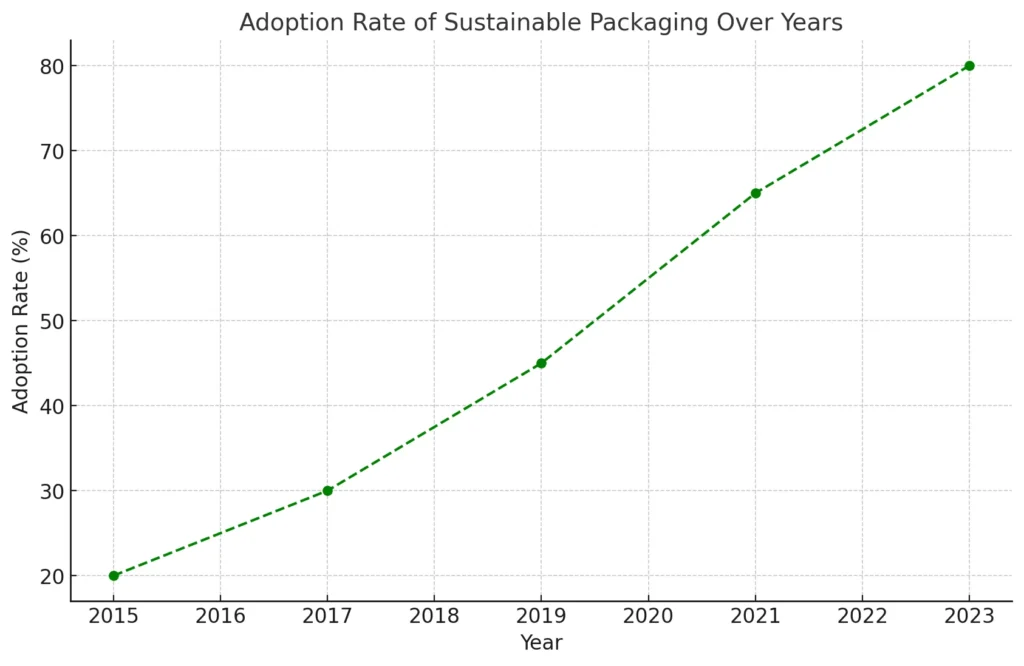
Adoption of Sustainable Packaging Over Time
The chart below shows how sustainable packaging adoption has grown over the years.
Challenges in Packaging
- Environmental Concerns:
- Plastic pollution and waste are major issues.
- Cost:
- High-quality or sustainable materials can be expensive.
- Durability:
- Balancing lightweight designs with durability is tricky.
Conclusion
Packaging is an essential part of our daily lives. It protects products, communicates important information, and plays a big role in marketing. With the rise of sustainable practices, the future of packaging is about balancing functionality and environmental responsibility.
By understanding packaging, we can make better choices as consumers and contribute to a greener world.
Call to Action
Are you choosing sustainable packaging? Share your thoughts in the comments!

